Introduction
The Domain Name System (DNS) is a fundamental component of the internet, playing a crucial role in translating human-readable domain names into IP addresses that computers use to communicate. Without DNS, users would have to memorize numerical IP addresses instead of simply typing a domain name like “example.com” into their web browsers.
Understanding how DNS services work and the different types available is essential for individuals and businesses looking to optimize website performance, security, and reliability. This article will explore the workings of DNS, the various DNS services available, and why they matter in today’s digital landscape.
Definition
A domain name system serves as a means of directing people to websites on the internet. To access a website, a user enters an easy-to-use name, like “google.com,” into their browser. With domain names serving as an address for locating particular web pages and online services, people can find and remember websites more easily.
How DNS Works
DNS functions as a distributed directory that maps domain names to IP addresses. The process involves multiple steps:
User Request: When a user enters a domain name into a browser, the system checks its local cache for the corresponding IP address.
Recursive Resolver Query: If the address is not in the cache, the request is sent to a DNS resolver, usually provided by the user’s Internet Service Provider (ISP).
Root Server Query: The resolver queries the root DNS server, which directs it to the appropriate Top-Level Domain (TLD) server (e.g., .com, .net, .org).
TLD Server Query: The TLD server then points the resolver to the authoritative name server for the requested domain.
Authoritative Name Server: The authoritative server returns the IP address for the requested domain.
Response to User: The resolver caches the information and sends the IP address back to the browser, which then connects to the website’s server.
This process happens in milliseconds, ensuring seamless web browsing experiences.
Types of DNS Services
Several types of DNS services exist to fulfill different needs. Below are the main categories:
Recursive DNS Resolvers:
Recursive resolvers are responsible for handling DNS queries from end users. They search for the requested domain’s IP address through a series of queries until they retrieve the correct information. Examples include:
- ISP DNS Resolvers: Provided by internet service providers.
- Public DNS Resolvers: Offered by companies like Google (8.8.8.8, 8.8.4.4) and Cloudflare (1.1.1.1) to provide faster and more secure DNS resolution.
Authoritative DNS Servers:
Authoritative DNS servers store and provide DNS records for specific domains. They respond to queries with the final, authoritative answer rather than seeking it from other sources. Types include:
- Primary (Master) DNS Server: Maintains the original DNS records and updates secondary servers.
- Secondary (Slave) DNS Server: Holds a copy of the master server’s DNS records to improve redundancy and availability.
Public DNS Services:
Public DNS services offer alternative DNS resolution options for users seeking enhanced performance, security, and privacy. Some popular providers include:
- Google Public DNS: Known for speed and reliability.
- Cloudflare DNS: Offers security and privacy features with its 1.1.1.1 service.
- OpenDNS: Provides customizable filtering and security options.
Private DNS Services:
Private DNS services are used within enterprises and organizations to manage internal domain resolution. These services enhance security by restricting access to internal networks and preventing unauthorized DNS lookups.
Managed DNS Services:
Managed DNS providers offer DNS hosting services with advanced features such as load balancing, failover support, and DDoS protection. Businesses rely on these services to maintain high availability and reliability. Examples include:
- Amazon Route 53
- Cloudflare DNS
- DynDNS
Dynamic DNS (DDNS):
Dynamic DNS services update domain name records in real-time to accommodate changing IP addresses. This is useful for home networks, remote access, and small businesses that do not have static IP addresses. Popular DDNS providers include:
- No-IP
- DynDNS
- DuckDNS
Why DNS Services Matter
DNS services impact several key aspects of online experiences, including:
Performance Optimization:
Fast DNS resolution improves website load times, reducing latency for users. Choosing a high-performance DNS provider can enhance overall browsing experiences.
Security Enhancements:
DNS plays a critical role in cybersecurity by preventing phishing, malware distribution, and DNS spoofing attacks. Secure DNS services, such as DNSSEC (Domain Name System Security Extensions), help verify the authenticity of DNS responses.
Redundancy and Reliability:
A well-configured DNS service ensures uptime and availability. Using multiple DNS servers or managed DNS services can help prevent downtime caused by server failures or cyberattacks.
Customizability and Control:
Businesses can use DNS filtering to restrict access to certain websites, enforce security policies, and improve network management.
Privacy Considerations:
Some DNS providers offer privacy-focused services that do not log user queries, protecting individuals from data tracking and potential exploitation.
Future Trends of Domain Name System (DNS) Service Market
Increased Adoption of Cloud-Based DNS Services:
Cloud-based DNS services are gaining popularity due to their scalability, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. Organizations are shifting from traditional on-premises DNS solutions to cloud-based models to enhance performance and reduce latency. Companies such as Google Cloud DNS and Amazon Route 53 are leading this transformation.
Enhanced Security Measures and DNS Protection:
With the rising number of cyber threats, DNS security has become a top priority. DNS-layer security solutions, such as DNS filtering, DNSSEC (DNS Security Extensions), and AI-driven threat detection, are being integrated to prevent cyberattacks, phishing, and domain hijacking. More businesses are investing in secure DNS services to protect sensitive data and prevent downtime.
Growth of Edge Computing and 5G Networks:
The expansion of edge computing and 5G networks is significantly influencing the DNS market. With lower latency and faster data processing, edge computing requires more efficient and resilient DNS services. 5G networks are further driving demand for DNS solutions that can handle increased data traffic and provide seamless connectivity.
Increasing Demand for Managed DNS Services:
As businesses seek to optimize their network performance, the demand for managed DNS services is growing. Managed DNS providers offer high availability, automatic failover, and global traffic management, helping companies ensure uninterrupted access to their digital assets.
Rising Adoption of AI and Automation in DNS Management:
Artificial intelligence and automation are playing a crucial role in the future of DNS services. AI-driven DNS management tools help organizations analyze traffic patterns, detect anomalies, and optimize DNS performance automatically. Automated DNS solutions also reduce manual configuration errors and improve overall efficiency.
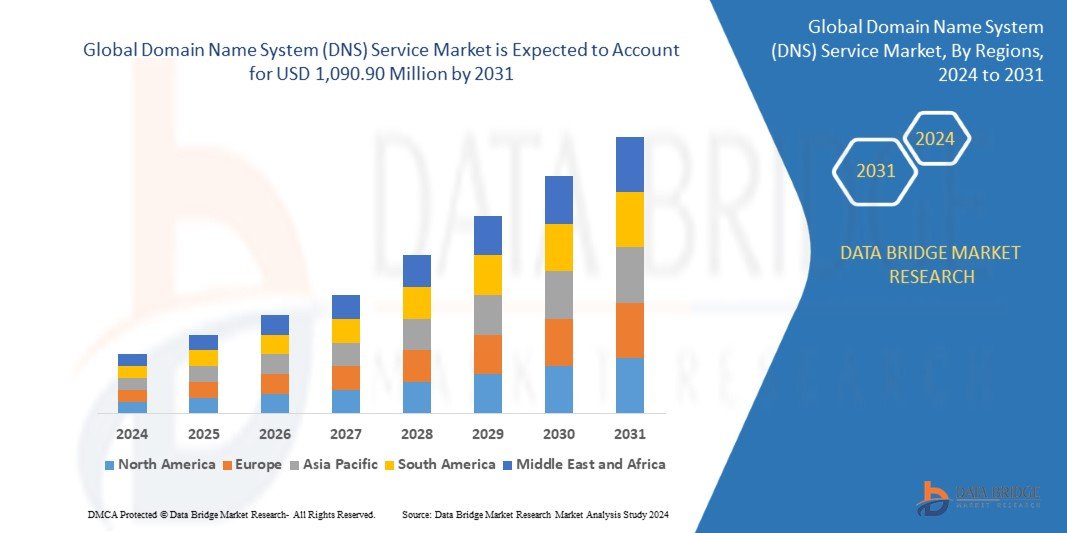
Growth Rate of Domain Name System (DNS) Service Market
According to Data Bridge Market Research, the global domain name system (DNS) service market, which was valued at USD 450.15 million in 2023, is anticipated to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.70% from 2024 to 2031, reaching USD 1,090.90 million.
Read More: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-dns-service-market
Conclusion
DNS services are a fundamental aspect of internet functionality, impacting website accessibility, security, and performance. Understanding how DNS works and choosing the right type of DNS service can enhance browsing experiences, protect against cyber threats, and ensure network reliability. Whether for personal use, enterprise security, or website management, selecting a suitable DNS provider is crucial in today’s digital landscape.